| [1] Lange A,Kasperk C,Alvares L,et al.Survival and Cost Comparison of Kyphoplasty and Percutaneous Vertebroplasty Using German Claims Data.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013; 39(4): 318-326.
[2] Liu J,Li X,Tang D,et al.Comparing pain reduction following vertebroplasty and conservative treatment for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Pain Physician. 2013;16(5): 455-464.
[3] Kim JH,Yoo SH.Long-term Follow-up of Percutaneous Vertebroplasty in Osteoporotic Compression Fracture: Minimum of 5 Years Follow-up. Asian Spine J. 2012; 6(1): 6-14.
[4] Kim KW,Cho KJ,Kim SW,et al.A nation-wide, outpatient-based survey on the pain, disability, and satisfaction of patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures.Asian Spine J. 2013;7(4):301-307.
[5] Chen D,An ZQ,Song S,et al.Percutaneous vertebroplasty compared with conservative treatment in patients with chronic painful osteoporotic spinal fractures.J Clin Neurosci. 2014; 21(3):473-477.
[6] Lee YK,Jang S,Lee HJ,et al.Mortality after vertebral fracture in Korea: analysis of the National Claim Registry.Osteoporos Int.2012;23(7):1859-1865.
[7] 史光华,李鹏翠,卫小春.骨质疏松椎体压缩骨折的治疗进展[J].中国骨伤, 2013,26(10):878-882.
[8] Wu ZX,Gao MX,Sang HX,et al.Surgical treatment of osteoporotic thoracolumbar compressive fractures with open vertebral cement augmentation of expandable pedicle screw fixation: a biomechanical study and a 2-year follow-up of 20 patients. J Surg Res.2012;173(1):91-98.
[9] Yu CW,Hsieh MK,Chen LH,et al.Percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty for the treatment of vertebral compression fractures. BMC Surg.2014;14:3.
[10] 柳申鹏,刘中何,赵斌,等.骨水泥植入经皮椎体成形治疗胸腰椎体骨折[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(29):5465-5468.
[11] 徐建成,白靖平,锡林宝勒日,等.注入骨水泥椎体成形与非手术治疗骨质疏松性椎体压缩骨折的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(13):2366-2370.
[12] Hulme PA,Krebs J,Ferguson SJ,et al.Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty: a systematic review of 69 clinical studies.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2006;31(17):1983-2001.
[13] Chen WJ,Kao YH,Yang SC,et al.Impact of cement leakage into disks on the development of adjacent vertebral compression fractures. Journal of spinal disorders & techniques. 2010;23(1):35-39.
[14] Chen X,Ren J,Zhang J,et al.Impact of Cement Placement and Leakage in Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures Followed by Percutaneous Vertebroplasty. J Spinal Disord Tech.2013.[Epub ahead of print]
[15] Venmans A,Lohle P,Van Rooij W,et al.Frequency and outcome of pulmonary polymethylmethacrylate embolism during percutaneous vertebroplasty.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008;29(10):1983-1985.
[16] Ha KY,Kim YH,Chang DG,et al.Causes of late revision surgery after bone cement augmentation in osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures.Asian Spine J.2013;7(4): 294-300.
[17] He SC,Teng GJ,Deng G,et al.Repeat vertebroplasty for unrelieved pain at previously treated vertebral levels with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2008;33(6):640-647.
[18] 吴梅祥,白波,吴景明,等.骨质疏松椎体压缩性骨折椎体成形术后失败的原因与对策[J].中国创伤骨科杂志,2011,13(9):893-895.
[19] Nieuwenhuijse MJ,Van Erkel AR,Dijkstra PD.Cement leakage in percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: identification of risk factors.Spine J.2011;11(9):839-848.
[20] Nieuwenhuijse MJ,Muijs SP,van Erkel AR,et al.A clinical comparative study on low versus medium viscosity polymethylmetacrylate bone cement in percutaneous vertebroplasty: viscosity associated with cement leakage. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2010; 35(20):E1037-1044.
[21] Baroud G,Crookshank M,Bohner M.High-viscosity cement significantly enhances uniformity of cement filling in vertebroplasty: an experimental model and study on cement leakage.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2006;31(22):2562-2568.
[22] Anselmetti GC,Zoarski G,Manca A,et al.Percutaneous vertebroplasty and bone cement leakage: clinical experience with a new high-viscosity bone cement and delivery system for vertebral augmentation in benign and malignant compression fractures.Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2008; 31(5):937-947.
[23] 李春海,刘尚礼,叶伟,等.高黏度骨水泥在经皮椎体成形术中的应用[J].中华骨科杂志,2007,27(4):259-262.
[24] Stevenson M,Gomersall T,Lloyd Jones M,et al.Percutaneous vertebroplasty and percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty for the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral fractures: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis.Health Technol Assess.2014;18(17):1-290.
[25] Xing D,Ma JX,Ma XL,et al.A meta-analysis of balloon kyphoplasty compared to percutaneous vertebroplasty for treating osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures.J Clin Neurosci.2013;20(6):795-803.
[26] 蔺福辉,易小波,任志宏.高粘度骨水泥在椎体成形术中的应用[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂,2009,24(1):66-67.
[27] Bergmann M,Oberkircher L,Bliemel C,et al.Early clinical outcome and complications related to balloon kyphoplasty. Orthop Rev (Pavia).2012;4(2):e25.
[28] Georgy BA.Feasibility, safety and cement leakage in vertebroplasty of osteoporotic and malignant compression fractures using ultra-viscous cement and hydraulic delivery system.Pain Physician.2012;15(3):223-228.
[29] 彭小忠,陈明,武振国,等.经皮椎体成形102例中22例骨水泥渗漏原因[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(8):1515-1518.
[30] Lee MJ,Dumonski M,Cahill P,et al.Percutaneous treatment of vertebral compression fractures: a meta-analysis of complications.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2009; 34(11):1228-1232.
[31] 王永祥,王广斌,王静成,等.椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体骨折的并发症及防治[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2010,16(11):855-858.
[32] Lee KA,Hong SJ,Lee S,et al.Analysis of adjacent fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty: does intradiscal cement leakage really increase the risk of adjacent vertebral fracture? Skeletal Radiol.2011;40(12):1537-1542.
[33] Komemushi A,Tanigawa N,Kariya S,et al.Percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic compression fracture: multivariate study of predictors of new vertebral body fracture.Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol.2006;29(4):580-585.
[34] 汪宇,刘先银,郭建恩,等.椎体后凸成形与后伸体位恢复骨质疏松性压缩骨折椎体高度12例[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2009,13(26):5167-5170. |
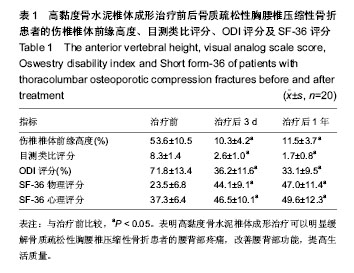
.jpg)
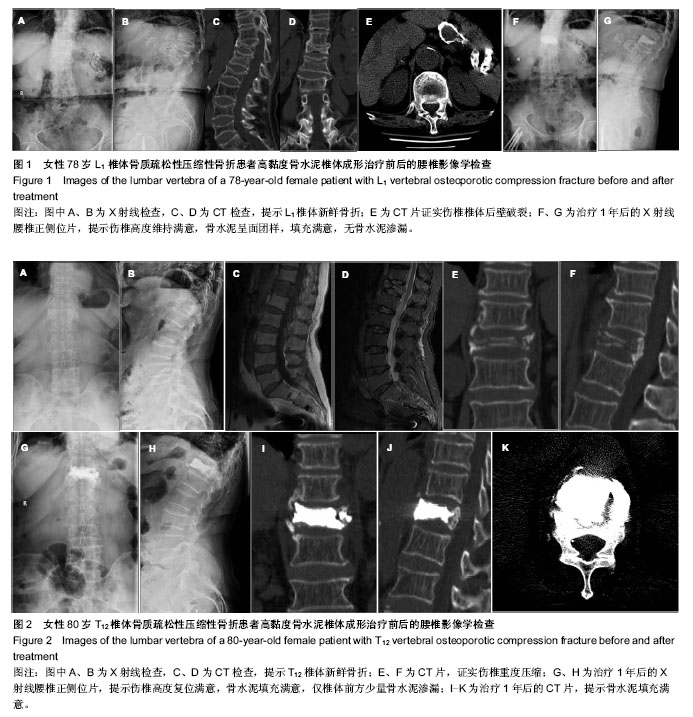
.jpg)